Understanding the cost dynamics of industrial metal shredders is crucial for businesses involved in recycling, waste management, or metal processing. These machines are pivotal in reducing large metal materials into smaller, manageable pieces, and investing in the right shredder can significantly impact operational efficiency and profitability.
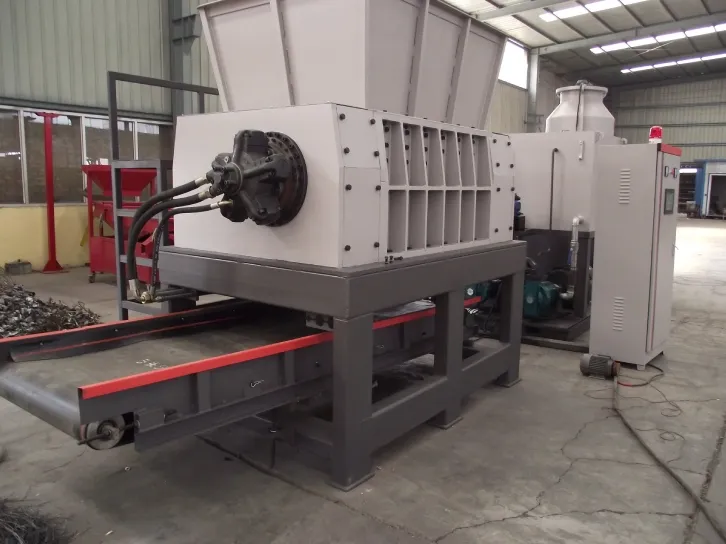

To navigate the complexities of industrial metal shredder pricing, it is critical to delve into factors influencing costs and to leverage insights from industry experts. The cost of an industrial metal shredder is primarily influenced by the shredder's capacity, type, brand reputation, and technological features.
Firstly, the capacity of a shredder, measured by the volume of metal it can process per hour, significantly affects its price. Shredders with higher capacities generally come with higher price tags due to their robust build and enhanced power. For instance, a small-scale shredder suitable for limited operations might cost between $10,000 to $50,000, while larger, high-capacity models designed for heavy-duty industrial use can start from $500,000 and go up to several million dollars.
Secondly, the type of shredder is another determining factor. There are different types of industrial metal shredders, such as hammer mills, twin-shaft shredders, and granulators. Hammer mills, known for their aggressive shredding power, are suitable for heavy-duty processing and typically command a higher price due to their capability to handle a wide variety of metals and their durability. On the other hand, twin-shaft shredders offer precision and efficiency, ideal for applications requiring meticulous shredding, and may vary in pricing based on their specific functionalities.
The brand reputation and geographical origin of the shredder also play substantial roles in pricing. Established brands with a proven track record of reliability and performance often charge premium prices. These brands justify their pricing by providing superior technology, comprehensive after-sales services, and longer warranty periods that reassure buyers of their investment's longevity.
industrial metal shredder cost
Additionally,
the technological features integrated into a shredder can increase costs. Advanced shredders equipped with automation, remote monitoring, and AI-driven systems facilitate user-friendly operations and improved efficiency but come at a higher cost. Such cutting-edge features allow businesses to optimize their shredding processes, reduce manual oversight, and enhance safety, making them a worthwhile investment for many enterprises.
An authoritative perspective is essential when considering these costs. Industry veterans emphasize performing a detailed cost-benefit analysis before purchasing an industrial metal shredder. Factors such as the specific types of metal to be processed, available budget, and anticipated throughput should be thoroughly evaluated to select a shredder that aligns with business objectives. Consulting with consultants and engineers specializing in industrial machinery can provide valuable insights and help tailor choices to meet specific needs.
To build trustworthiness, it's crucial to highlight after-purchase considerations. Long-term maintenance costs, availability of spare parts, and technician accessibility should be factored into the total cost of ownership. Many reputable suppliers offer maintenance agreements and training for operational staff to ensure the shredder performs at its peak efficiency while minimizing downtime.
In conclusion, while the initial expenditure for an industrial metal shredder may seem substantial, a strategic investment in the right shredder offers considerable returns in the form of improved productivity, operational efficiency, and potentially reduced costs in metal waste management. Businesses should prioritize thorough research and seek expert guidance to ensure their investment is future-proof and aligned with their operational requirements. Expert recommendations and robust after-sales support can spell the difference between a costly burden and a profitable asset in the industrial landscape.


