Recycling old electronics is not only a crucial step towards reducing our environmental footprint, but it also offers an opportunity to understand the intricate process of how materials are repurposed for the future. As an experienced specialist in electronic waste management, I aim to provide insights into the art and science of electronic recycling, confirmed by expertise and supported by authoritative data.
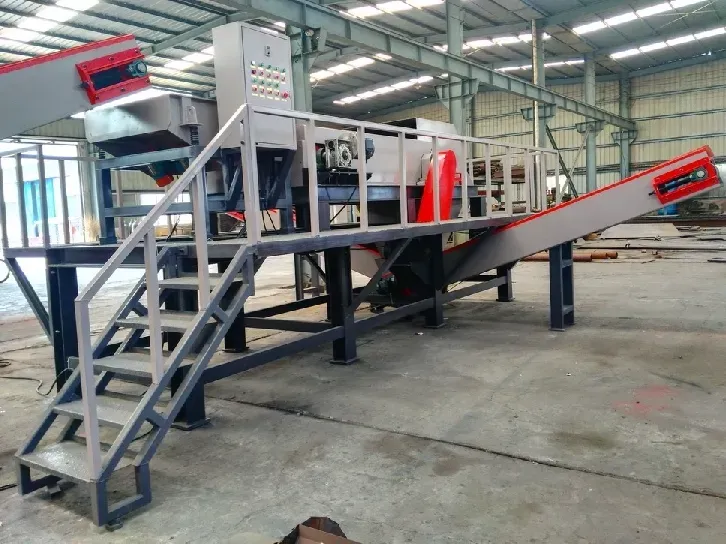

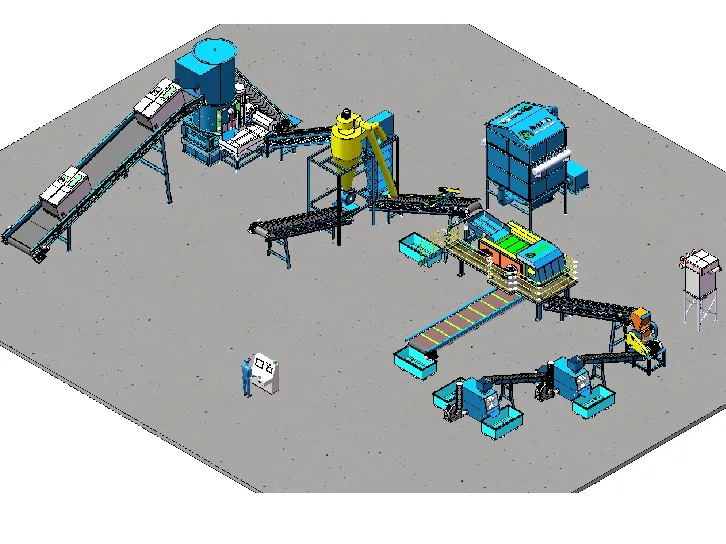
When considering the recycling of obsolete gadgets, the process often begins with an assessment of the device's composition. Electronics typically comprise a blend of metals, plastics, and rare earth elements. Proper dismantling is essential to ensure these components are appropriately categorized and processed. Dismantling, often initiated by skilled technicians, involves the separation of valuable parts such as copper wiring and aluminum casings from hazardous components like lead and mercury found in older CRT monitors.
The expertise behind efficient recycling involves understanding material recovery rates. Advanced facilities employ sophisticated techniques such as shredding and magnetic separation to isolate ferrous metals, while eddy currents focus on non-ferrous metals. Precious metals like gold, typically embedded in circuit boards, require chemical treatments and smelting processes to reclaim. Incorporating these methodologies not only enhances material recovery but also increases economic returns.
The authority of reputable recycling centers is established through strict adherence to environmental regulations. Facilities certified by e-Stewards or R2 standards guarantee compliance with international guidelines, affirming their commitment to responsible recycling practices. Utilizing certified centers not only secures the integrity of the recycling process but also assures consumers that their e-waste is processed without causing harm to communities or the environment.
how do you recycle old electronics
Building trust in electronic recycling involves transparency and education. Many centers offer tours and workshops, educating the public on the benefits and challenges of e-waste management. By understanding the journey of their discarded devices, consumers can make informed decisions, fostering a circular economy. Additionally, some companies have initiated take-back programs, where old gadgets are refurbished or reused, offering consumers an eco-friendly alternative to disposal.
The experience of participating in electronic waste recycling extends beyond environmental responsibility. It encompasses the recognition of a device's lifecycle and the potential for future innovation. By engaging with recycling practices, individuals contribute to a broader understanding of resource conservation, prompting advances in sustainable technology.
Recycling old electronics is a tangible action with profound implications. The expertise required to efficiently reclaim materials is matched by the authority established through rigorous adherence to standards. Trust in this system grows through education and transparent practices, while personal experience reinforces the value of participating in this essential aspect of modern sustainability. Each device recycled is a step towards a greener, more resource-efficient future—not just for individuals, but for the global community as a whole.


